Topic 6. Stock exchanges in the Asian region
| Сайт: | Навчально-інформаційний портал НУБіП України |
| Курс: | International Exchange Activities ☑️ |
| Книга: | Topic 6. Stock exchanges in the Asian region |
| Надруковано: | Гість-користувач |
| Дата: | понеділок, 9 березня 2026, 15:41 |
1. Common features
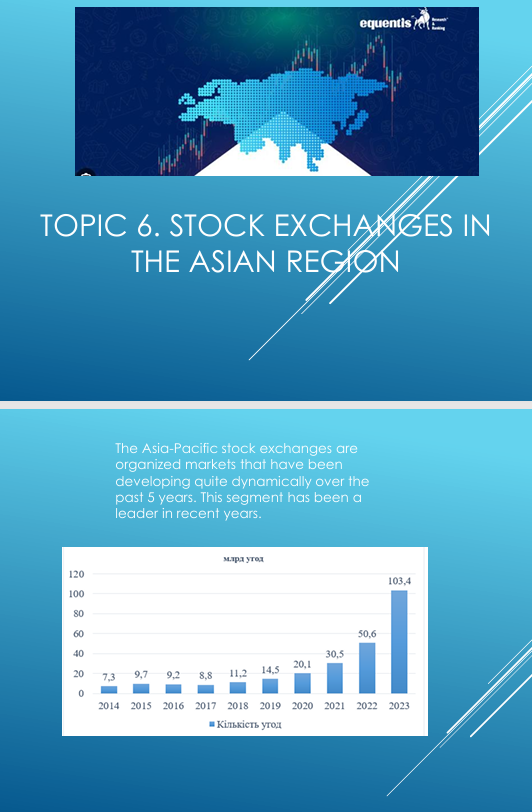
The Asia-Pacific stock exchanges are organized markets that have been developing quite dynamically over the past 5 years. This segment has been a leader in recent years.
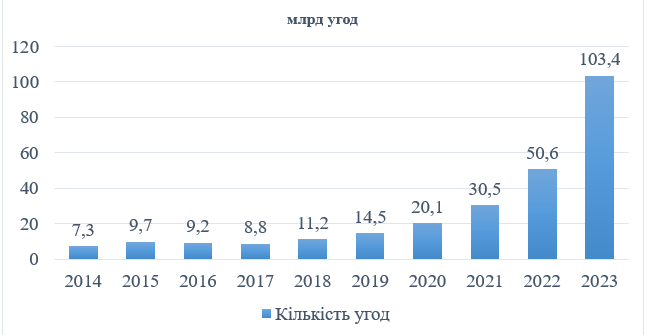
According to the Futures Industry Association, the dynamics of international exchange trading in these markets indicate growth in the last 5 years.
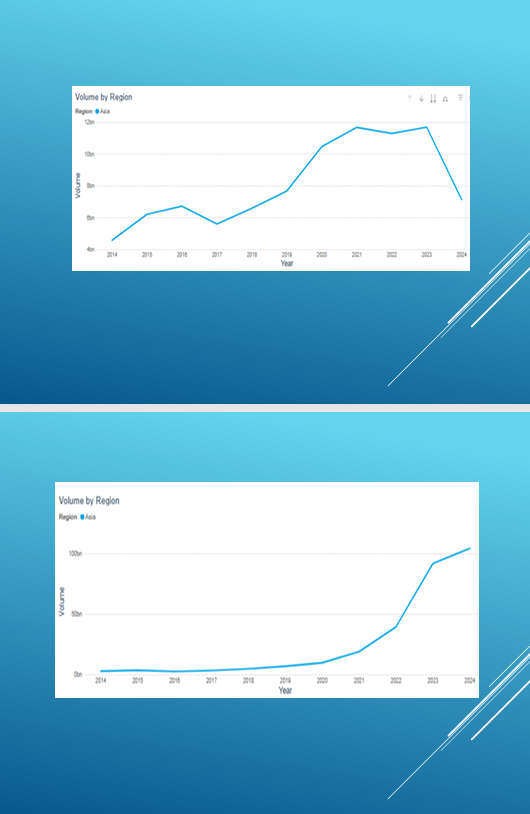
In 2023, the volume of exchange trading on exchange platforms in the Asia-Pacific region reached a record level of 103.4 billion transactions, which is 14.2 times higher than in 2014, when 7.3 billion transactions were recorded.
Over the past three years, record figures for concluded transactions have been recorded on exchanges. At the same time, exchange trading in futures contracts is significantly lower than options trading in recent years. Thus, futures trading in 2023 amounted to 11.7 billion transactions, and options trading - 91.7 billion transactions.
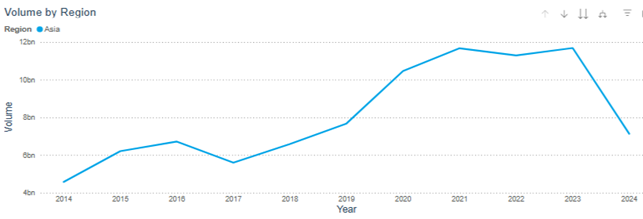
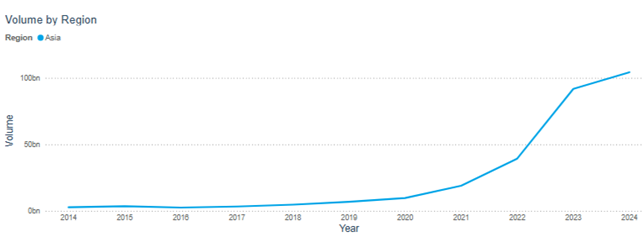
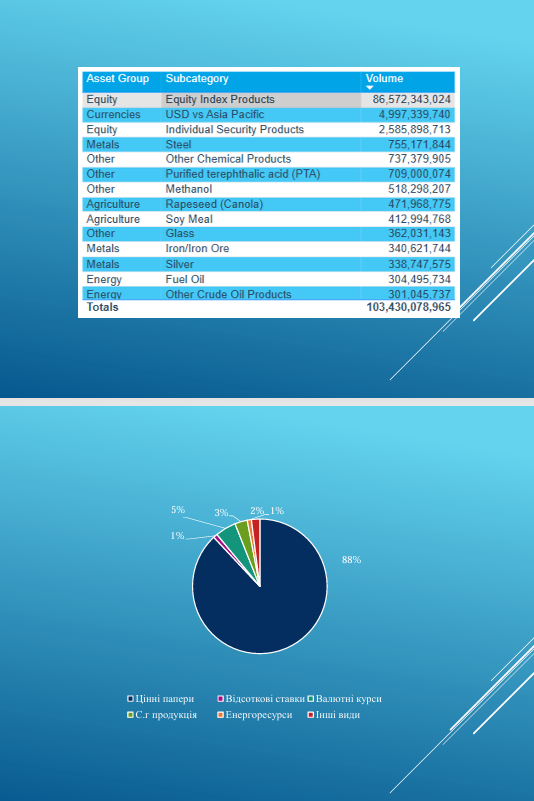
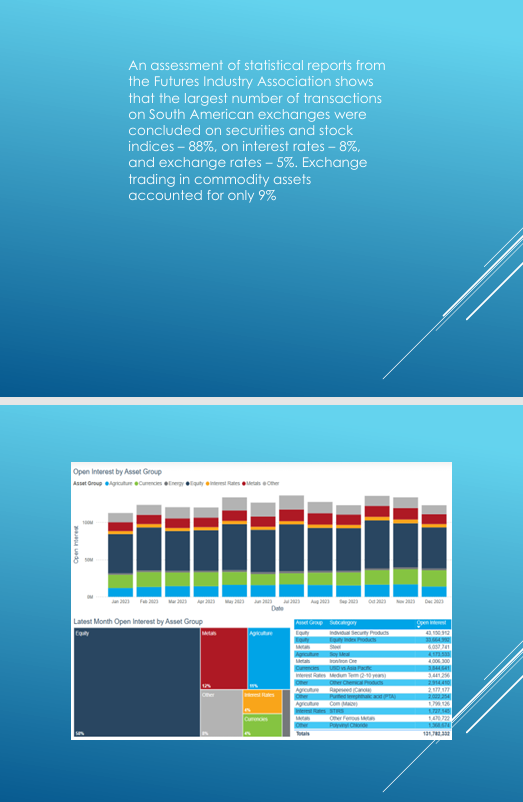
An assessment of statistical reports from the Futures Industry Association shows that the largest number of transactions on South American exchanges were concluded on securities and stock indices – 88%, on interest rates – 8%, and exchange rates – 5%. Exchange trading in commodity assets accounted for only 9%.
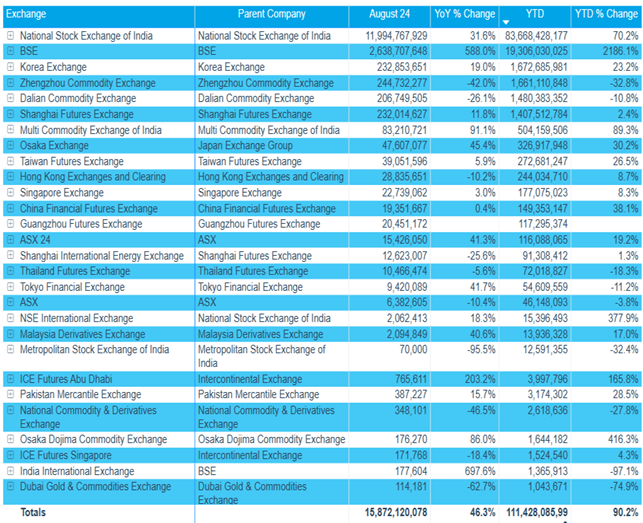
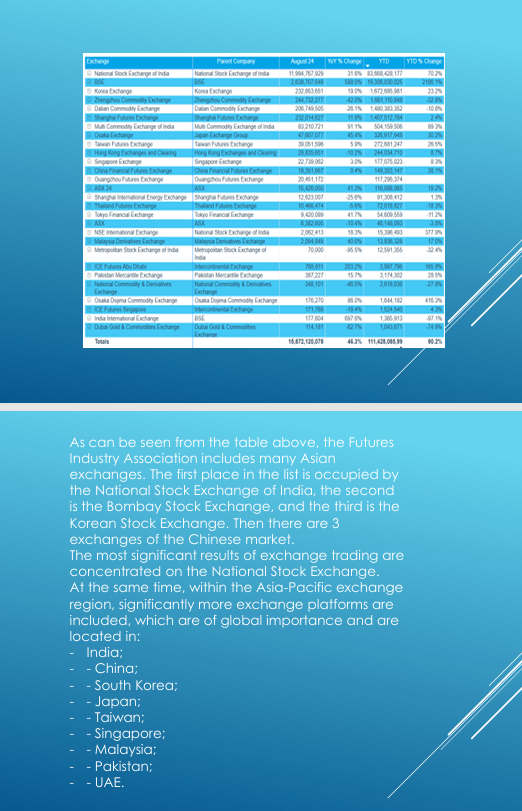
As can be seen from the table above, the Futures Industry Association includes many Asian exchanges. The first place in the list is occupied by the National Stock Exchange of India, the second is the Bombay Stock Exchange, and the third is the Korean Stock Exchange. Then there are 3 exchanges of the Chinese market [16].
The most significant results of exchange trading are concentrated on the National Stock Exchange.
At the same time, within the Asia-Pacific exchange region, significantly more exchange platforms are included, which are of global importance and are located in:
- India;
- China;
- South Korea;
- Japan;
- Taiwan;
- Singapore;
- Malaysia;
- Pakistan;
- UAE.
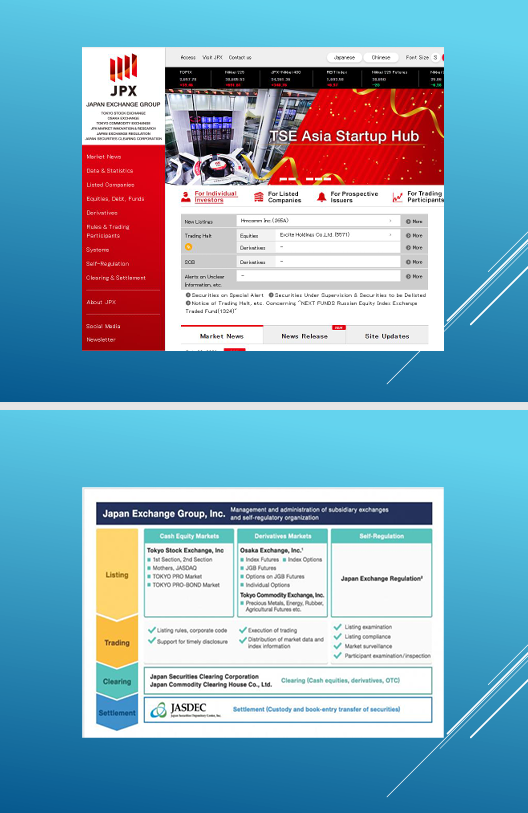
2. Japan Exchange Group
For a long time, the Tokyo Stock Exchange played an important role in the Asian stock market. However, in Japan, a large number of exchanges operated on the stock market, different in terms of types of assets. They are now united in the Japan Exchange Group exchange alliance.
Japan Exchange Group Inc. (JPX) was the result of the merger of Tokyo Stock Exchange Group and Osaka Securities Exchange in 2013.
In 2019, JPX expanded through the acquisition of Tokyo Commodity Exchange Inc.
Today, the Japan Exchange Group Inc. exchange alliance includes several segments:
- Tokyo Stock Exchange;
- Osaka Exchange;
- Tokyo Commodity Exchange;
- Clearing House;
- Innovation and Research Division;
- JPX Regulatory Division.

JPX organizes exchange trading and provides open access to exchange-traded instruments listed on it. The Tokyo Stock Exchange also provides clearing and settlement services, as well as analytical reports on the results of exchange trading.
The Tokyo Mercantile Exchange, which is part of this alliance, was founded in 1984 as an exchange on which gold and other commodity assets were traded - textiles, rubber.
The Tokyo Mercantile Exchange currently specializes in trading energy resources:
- oil;
- gasoline;
- gas oil;
- kerosene;
In addition, the Tokyo Mercantile Exchange provides trading in metals:
- silver;
- gold;
- palladium;
- platinum.
The main stock index of this platform is the world-famous Nikkey-TOCOM index.
3. Developing stock markets in the Asian region
The Asia-Pacific stock market region has been playing a significant role in international stock market activity in recent years.
The National Stock Exchange of India has been ranked first in the top 10 international stock markets in recent years. The volume of stock market trading on this exchange has increased dramatically in the last five years and in 2023 recorded a new level of 84.8 billion transactions, which is 14 times higher than in 2019.
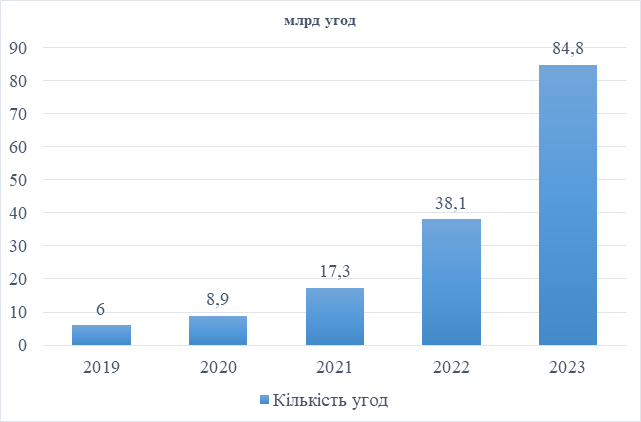
The National Stock Exchange of India was founded in 1992 and is located in Mumbai. It is currently one of the three largest stock exchanges in the world, along with the American stock exchanges NYSE and NASDAQ [44].
In 1995, the National Stock Exchange of India introduced a fully automated electronic trading system. Today, there are over 2,200 issuers on the exchange. Several key stock indices, the Nifty 50, CNX 100 and CNX 500, are listed on the exchange, as well as the FMCG index for IT companies.
The National Stock Exchange of India has an integrated electronic business model that includes a listing, clearing and settlement services, stock indices, information resources, technology solutions, etc. The exchange also supervises compliance with trading and clearing procedures, which are listed in the trading rules and regulations of the exchange.
The National Stock Exchange of India is a leader in innovative solutions, as the exchange adds new types of investment instruments every year.
In 2003, the exchange made another technological breakthrough by launching retail trading on its electronic platforms. This allowed it to attract a large number of small investors to trade securities. The main advantage was the ability to not visit the exchange to conclude transactions.
In 2009, the National Stock Exchange of India proposed two important initiatives to expand the circle of its users. First, it launched the Mutual Fund Service System (MFSS), which simplified the management of mutual funds. Second, the exchange launched trading in derivative contracts on stock indices, which allowed exchange trading participants to better use them in managing price risks and investing free cash.
In 2010, the stock exchange introduced a draft depository receipts based on an already operational electronic trading system, which allowed interested foreign companies to raise capital on the Indian stock market through IPOs. The same year, the National Commodity & Derivatives Exchange Limited (NCDEX) was launched for trading commodity derivative contracts.Despite their long history and long-standing practice, Chinese exchanges have become competitive in international stock markets in the last ten years.
The Shanghai Stock Exchange is included in the ranking of the 10 largest exchanges. Shanghai has historically been a city - a financial center for securities trading in China.
In 1920-1921, the Shanghai Stock Exchange began its activities, which also attracted foreign investors to trade. The exchange provided the opportunity to trade in debt obligations, government bonds and financial futures [45].
Since the 1980s, stock trading in China has developed in tandem with the reform of the country's economic system. In 1984, corporate bonds appeared in Shanghai. Today, the Shanghai Stock Exchange has become a growing market for international stock trading.
4. Presentation

Шрифти
Розмір шрифта
Колір тексту
Колір тла
Кернінг шрифтів
Видимість картинок
Інтервал між літерами
Висота рядка
Виділити посилання
Вирівнювання тексту
Ширина абзацу